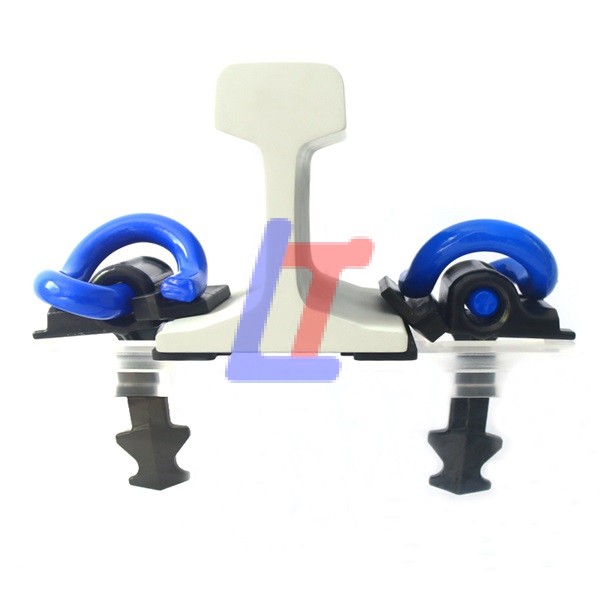
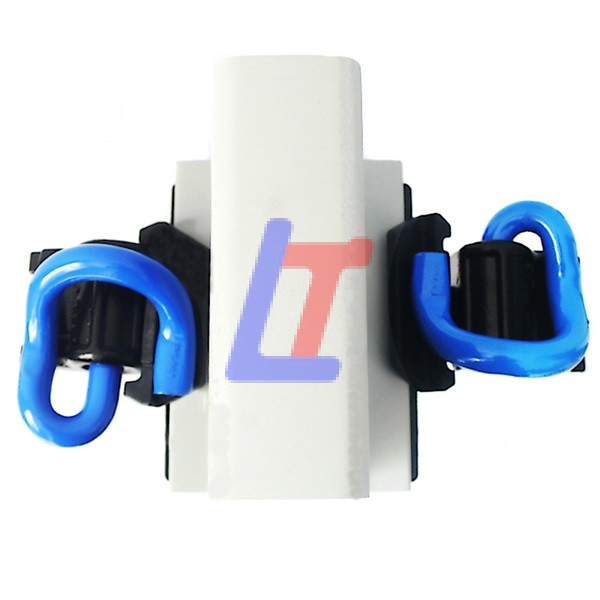
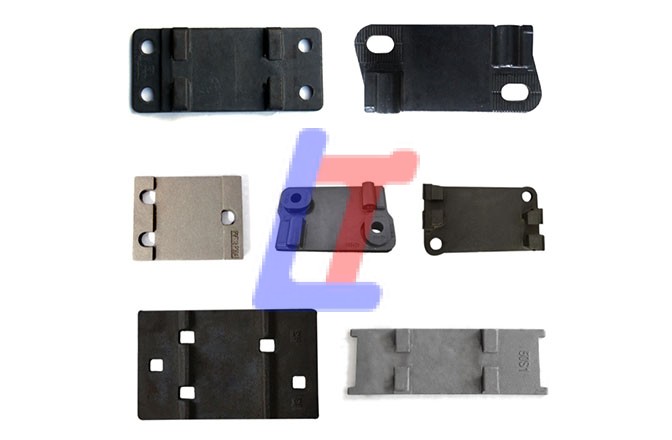
A Rail Clamp is a crucial component in modern rail fastening systems, designed to secure rails to sleepers (ties) while allowing for thermal expansion, vibration damping, and easy maintenance. It is widely used in ballasted, ballastless, and slab track systems for high-speed, heavy-haul, and urban transit applications.
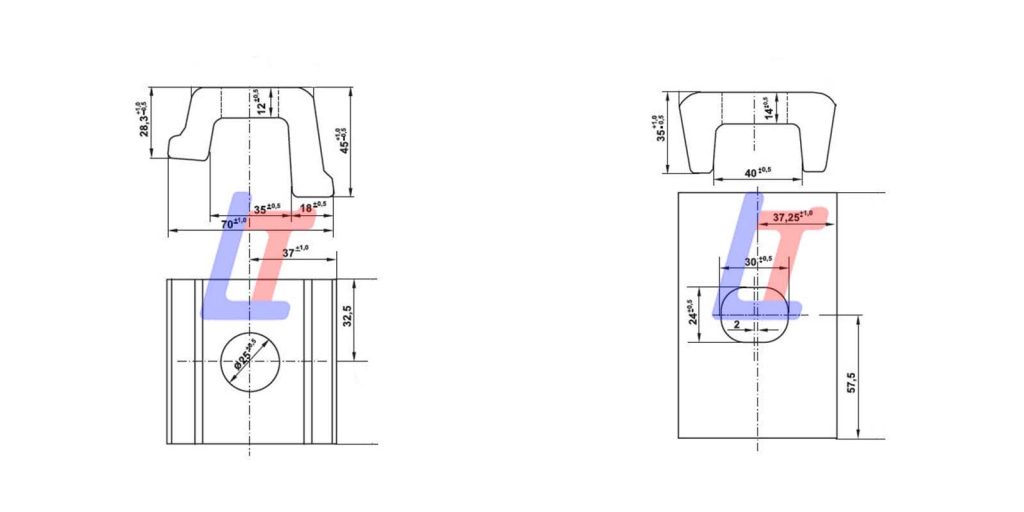
Key Features & Functions:
1.Secure Rail Holding:
- Clamps the rail foot to the baseplate/sleeper with controlled clamping force.
- Prevents vertical/lateral movement while permitting longitudinal expansion.
2.Elastic Design:
- Made from spring steel (60Si2MnA, 51CrV4) for fatigue resistance.
- Maintains constant tension despite dynamic loads and temperature changes.
3.Anti-Vibration & Anti-Corrosion
- Rubber pads or EVA inserts often paired with clamps to reduce noise/vibration.
- Zinc-plated, epoxy-coated, or stainless steel variants for harsh environments.
4.Fast Installation
- Compatible with e-clips, screw spikes, or wedge systems for quick assembly.
Types of Rail Clamp:
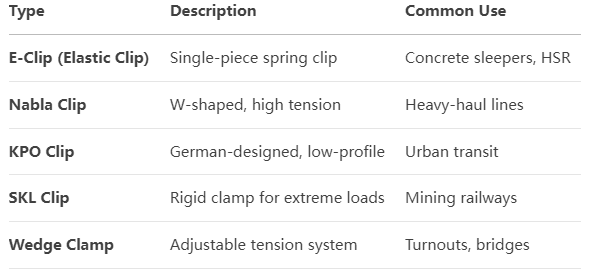
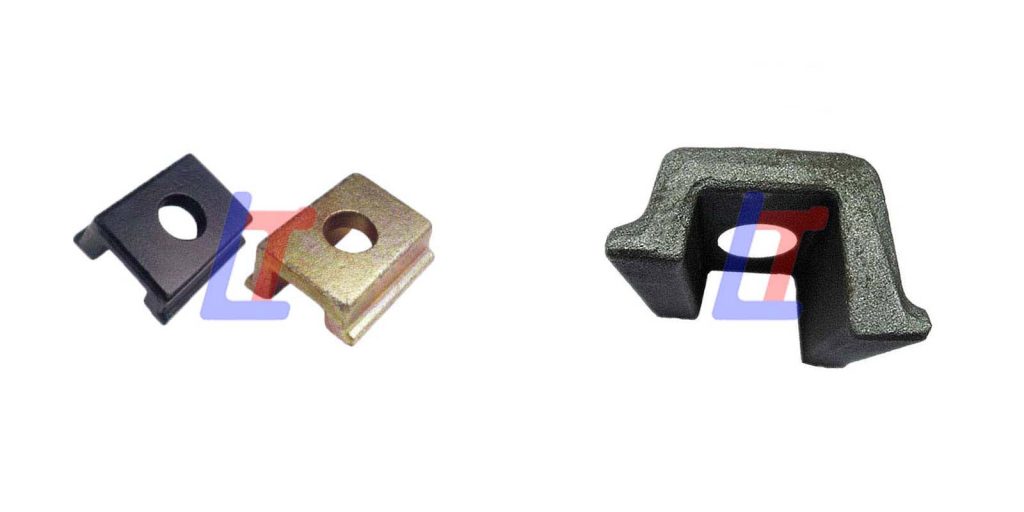
Installation & Maintenance:
1.Pre-Installation Checks:
- Verify rail alignment and baseplate condition.
- Clean rail foot/seating surface.
2.Installation Tools
- Hydraulic clip applicators (for mass installation)
- Manual clip hammers (for maintenance spots)
3.Torque Requirements
- Typical installation force: 2,000-3,500 N (E-clips)
- Wedge clamps: 100-150 Nm tightening torque
4.Replacement Indicators
- Visible cracks or deformation
- Loss of clamping force (>15% reduction)
- Corrosion penetrating >0.5mm depth
Advantages Over Traditional Fasteners
- 50% faster installation vs. bolt-and-nut systems
- Maintains tension despite rail wear/settling
- Reduces maintenance frequency by 3-5× vs. cut spikes
- No loose parts (critical for high-speed operations)
Industry Applications
- High-Speed Rail: Ensures stability at 300+ km/h
- Metro Systems: Minimizes vibration noise in tunnels
- Heavy Mining Railways: Withstands 40-ton axle loads
- Bridge Tracks: Accommodates expansion/contraction

















